Hair transplantation is a transformative solution for individuals experiencing hair loss, providing natural-looking results and renewed confidence. Who Is Not a Good Candidate for a Hair Transplant? However, not everyone is an ideal candidate for this procedure. Understanding who is not a good candidate for a hair transplant is essential to avoid unrealistic expectations, medical complications, and unsatisfactory outcomes. In this article, we will explore the key eligibility criteria, medical considerations, and circumstances that may make someone unsuitable for a hair transplant.
Table of Contents
ToggleHair Transplant Basics: Understanding the Procedure
Before examining who should avoid hair transplantation, it’s important to understand what the procedure entails. Hair transplants involve harvesting healthy hair follicles from a donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp, and transplanting them to thinning or balding regions. The two most common techniques are:
-
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): Also known as the strip method, this involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area and dissecting it into individual follicular units for transplantation.
-
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Individual follicles are harvested directly from the donor area and transplanted to the thinning areas, leaving minimal scarring.
While hair transplants can offer impressive results, their success depends heavily on patient selection. Not everyone qualifies for the procedure.
Key Criteria for Hair Transplant Candidates
Doctors evaluate several factors to determine a patient’s suitability for a hair transplant. While the procedure can help a wide range of individuals, the following criteria are generally considered essential:
-
Sufficient Donor Hair: Adequate, healthy hair in donor regions is crucial for transplantation. Individuals with sparse or thin donor areas may not achieve optimal results.
-
Stable Hair Loss: Patients whose hair loss is still progressing rapidly may not be ideal candidates, as ongoing shedding can compromise the longevity of the transplant.
-
Overall Health: Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of complications, making some patients unsuitable.
-
Realistic Expectations: Patients should have a clear understanding of what hair transplantation can achieve, including limitations in density and coverage.
Meeting these criteria helps ensure that the procedure is both safe and effective.
Who Is Not a Good Candidate for a Hair Transplant
There are several groups of individuals for whom hair transplantation may not be recommended. Understanding these limitations can help patients make informed decisions:
Individuals With Insufficient Donor Hair
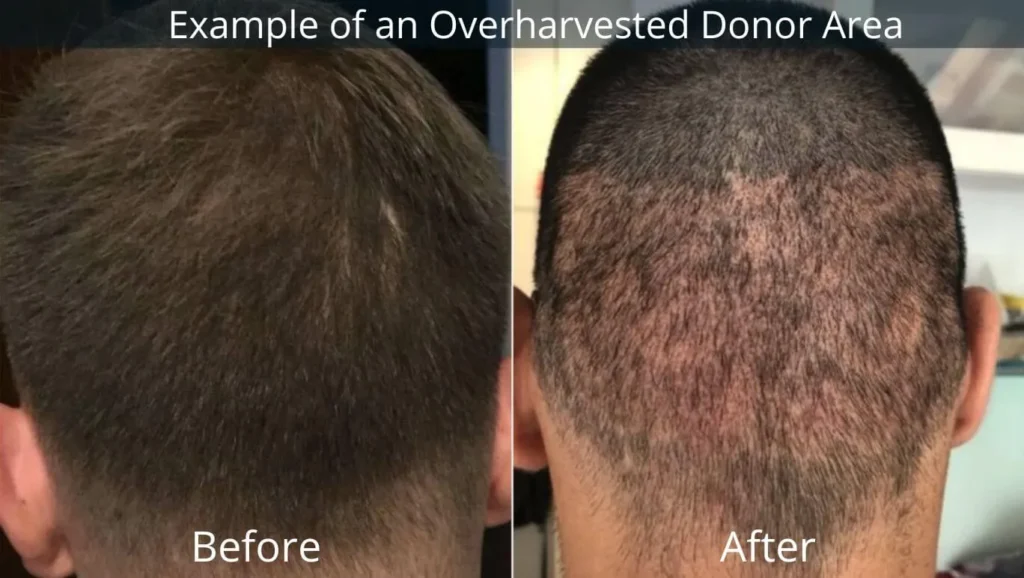
The success of a hair transplant relies on the availability of healthy hair follicles for transplantation. Patients with thin, sparse, or damaged donor areas may not have enough follicles to achieve the desired coverage. This is especially important in individuals with advanced balding patterns where donor hair is limited.
Patients With Unstable or Progressive Hair Loss
Hair loss that is ongoing or unpredictable can compromise transplant results. For example, someone with diffuse hair loss or young patients experiencing early-onset baldness may continue to lose hair after the procedure, making it difficult to maintain a natural appearance. Surgeons typically recommend waiting until hair loss stabilizes before undergoing transplantation.
Young Patients
Age plays a crucial role in transplant eligibility. Individuals under the age of 25 are often discouraged from undergoing hair transplantation because their hair loss patterns are still evolving. Transplanting hair too early may result in unnatural hairlines or the need for multiple procedures as hair loss progresses.
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Certain health conditions can make hair transplantation unsafe or less effective. These include:
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like alopecia areata can lead to unpredictable hair loss even after a transplant.
-
Bleeding Disorders: Patients with clotting issues may face higher risks during and after the procedure.
-
Heart or Circulatory Problems: Conditions that affect healing or blood flow can increase the likelihood of complications.
-
Chronic Illnesses: Uncontrolled diabetes or severe immune system deficiencies can interfere with recovery.
A thorough medical evaluation is essential to identify these risk factors.
Individuals With Scalp or Skin Conditions
Patients with certain scalp issues may not be ideal candidates for hair transplantation, including:
-
Scarring Alopecia: Permanent scarring can limit follicle survival and make transplantation difficult.
-
Severe Psoriasis or Dermatitis: Active inflammation can compromise healing and graft survival.
Treating or managing these conditions before considering a transplant is often recommended.
Unrealistic Expectations
Even patients with healthy donor hair and stable hair loss may not be ideal candidates if their expectations are unrealistic. Hair transplants can improve density and coverage but cannot replicate a full head of hair in severe cases. Understanding the limitations of the procedure is critical for patient satisfaction.
Common Misconceptions About Hair Transplant Eligibility
Many people assume that hair transplantation is suitable for anyone experiencing hair loss, but this is not the case. Common misconceptions include:
-
“I can get a transplant at any age”: Young patients often risk unnatural results if hair loss is not yet stabilized.
-
“FUE works even with sparse donor hair”: Both FUT and FUE require healthy, viable follicles; sparse donor areas can limit success.
-
“Hair transplants prevent future hair loss”: Transplants do not stop ongoing hair loss, and additional procedures may be needed.
-
“All hair loss types are suitable”: Conditions like alopecia areata or scarring alopecia may not respond well to transplantation.
Understanding these misconceptions helps potential patients make informed decisions and avoid disappointment. Beauty and wellness readers may also see Who Is Not a Good Candidate for Ketamine Therapy and Who Is Responsible for Littering From a Motor Vehicle.
How Surgeons Determine Suitability
Hair transplant specialists follow a structured evaluation process to identify who is not a good candidate:
-
Medical History Review: Assessing chronic illnesses, medications, and past surgeries.
-
Scalp Examination: Evaluating donor hair quality, scalp elasticity, and hair density.
-
Hair Loss Assessment: Determining pattern, progression, and stability of hair loss.
-
Patient Consultation: Discussing expectations, lifestyle, and post-operative care.
This thorough evaluation ensures that only suitable candidates proceed with surgery, maximizing safety and outcomes.
Alternatives for Those Unsuitable for Hair Transplants
For individuals who are not good candidates, several alternative treatments may be considered:
-
Medications: Finasteride and minoxidil can slow or prevent further hair loss.
-
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy: Stimulates natural hair growth using the patient’s own platelets.
-
Scalp Micropigmentation: Cosmetic tattooing to create the illusion of density.
-
Wigs and Hairpieces: Non-surgical options for coverage without medical intervention.
These alternatives allow patients to manage hair loss effectively while avoiding the risks associated with surgery.
Making the Right Choice
Hair transplantation can be life-changing for many individuals, but it is not suitable for everyone. Factors such as insufficient donor hair, unstable hair loss, young age, medical conditions, and unrealistic expectations can disqualify a person from being an ideal candidate. Consulting with a qualified hair transplant specialist is essential to determine suitability and explore alternative options when necessary. By understanding the limitations and requirements of hair transplantation, patients can make informed decisions, avoid unnecessary procedures, and achieve the best possible results, whether through surgery or alternative treatments. Ultimately, successful hair restoration is as much about choosing the right candidate as it is about the technical skill of the surgeon. Ensuring eligibility, health, and realistic expectations are the foundation of safe and satisfying hair transplant outcomes.